
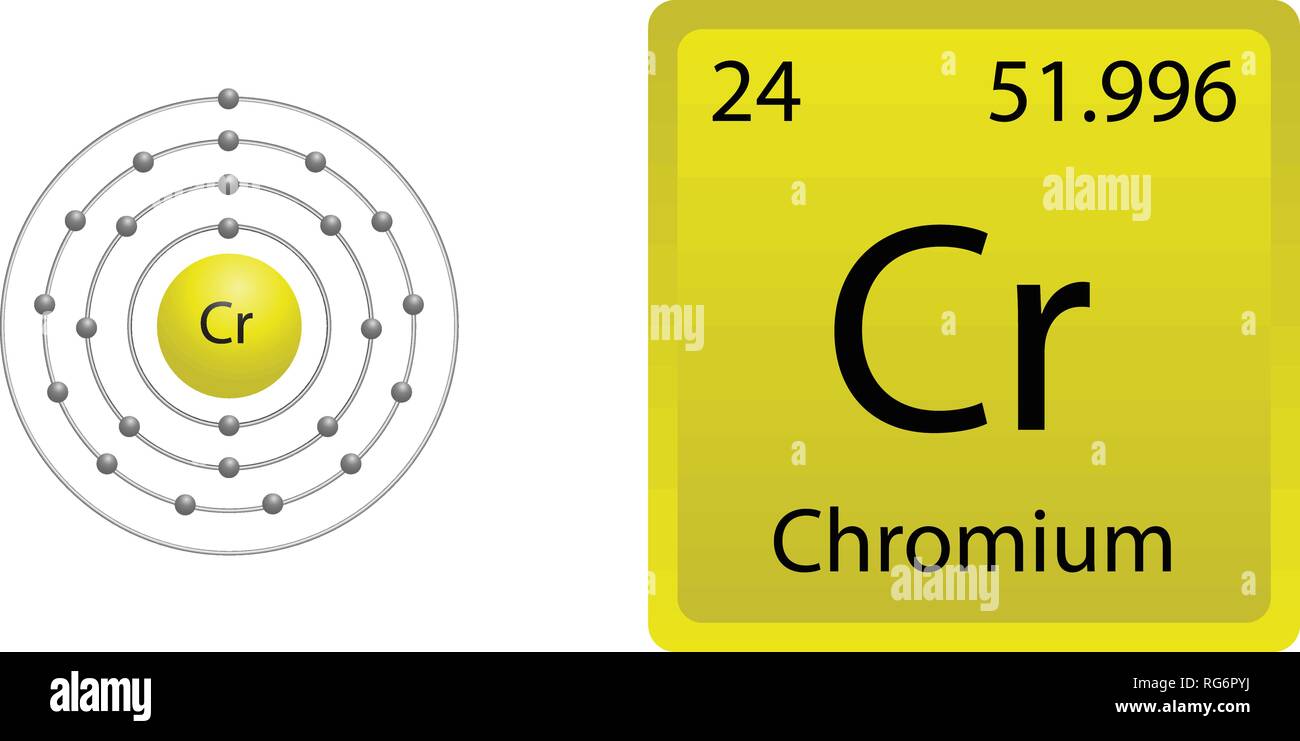
Further information is available in inorganic chemistry textbooks, usually at Level 1 or First Year University level. The terms low spin and high spin refer to the electronic configurations of particular geomtries of certain d-block metal ions. For electronic configurations, where it matters, the values given for octahedral species are low spin unless stated to be high spin. Size does depend upon geometry and environment. Its electron configuration can be represented as 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d. In this table, geometry refers to the arrangment of the ion's nearest neighbours. Chromium is a transition metal with atomic number 24, meaning it has 24 electrons. Match the correct orbital diagram to the correct species. Hartree-Fock wave functions and radial expectation values: hydrogen to lawrencium, LA-3691, Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, USA, 1968. Below are five possible orbital diagrams for the chromium atom and the chromium(III) ton. The R max values for neutral gaseous element valence orbitals are abstracted from reference 1. Image showing periodicity of valence s-orbital radius for the chemical elements as size-coded balls on a periodic table grid. For instance, the electron configurations (shown in Figure 6.29) of the transition metals chromium (Cr atomic number 24) and copper (Cu atomic number 29), among others, are not those. Table: valence shell orbital radii for chromium. An atom of the alkaline earth metal beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, contains four protons in the nucleus and four electrons surrounding the nucleus. Two values are given here, one is based upon calculations and the other upon observation - follow the appropriate link for further details. The problem is its meaning, which is clearly very different in different sources and books. The term "atomic radius" is not particularly helpful although its use is widespread.
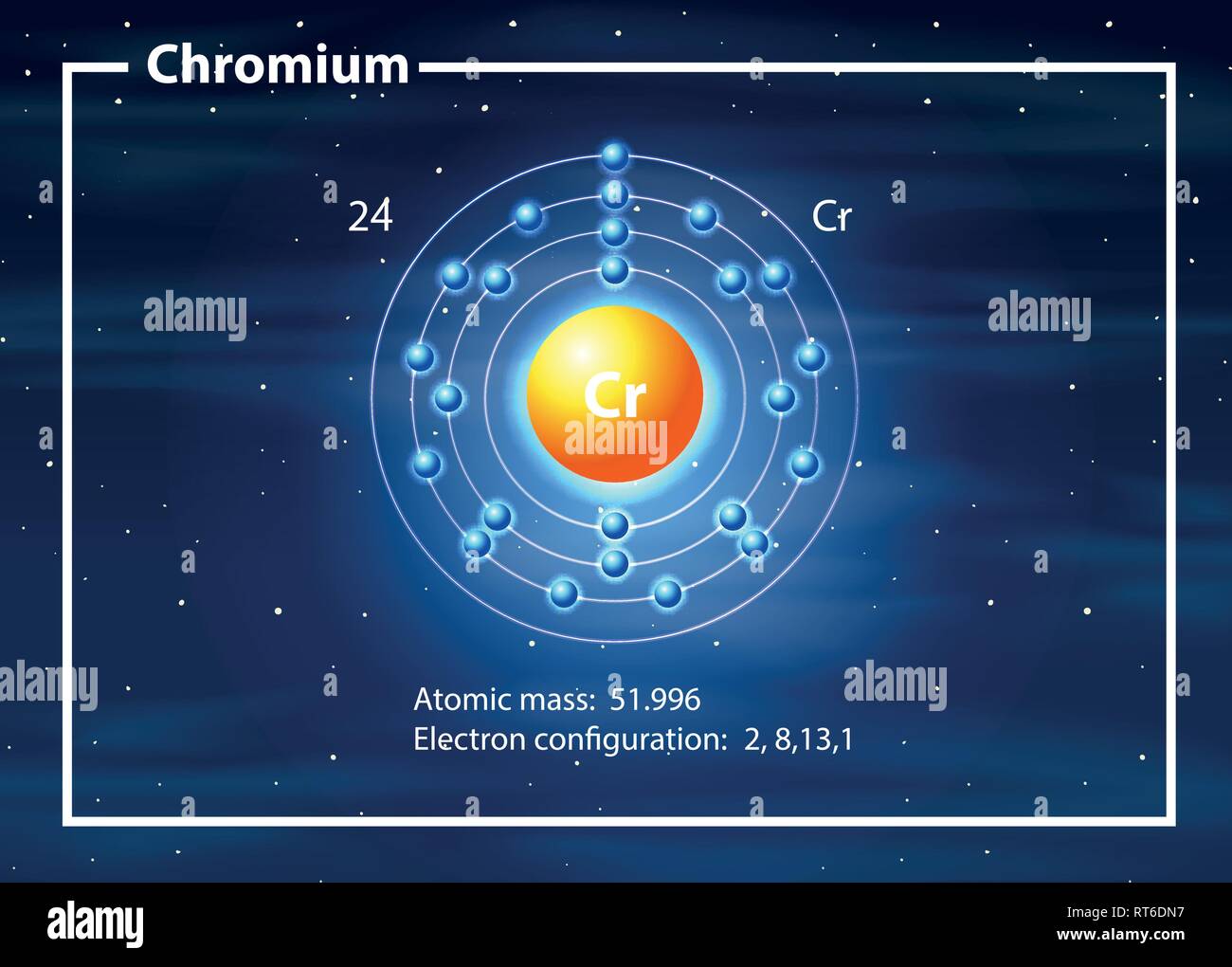
Other common ion of chromium include chromium of oxidation state 6 and 3. Follow the appropriate hyperlinks for definitions of each radius type. The equation that shows the formation of chromium (ii) ion from neutral chromium atom is as follow Cr -> cr2+ + 2e-Cr2+ is the chromium ion with oxidation state of two which is one of the common ion of chromium. The size of neutral atoms depends upon the way in which the measurement is made and the environment. All values of radii are given in picometres (pm). Follow the appropriate hyperlinks for literature references and definitions of each type of radius. If this atom loses one electron, it will become a cation with a 1+ charge (11 10 1+). For example, a neutral sodium atom (Z 11) has 11 electrons. Positively charged atoms called cations are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons. There are several other ways ways to define radius for atoms and ions. An atom that gains one or more electrons will exhibit a negative charge and is called an anion. It is not always easy to make sensible comparisons between the elements however as some bonds are quite short because of multiple bonding (for instance the O=O distance in O 2 is short because of the the double bond connecting the two atoms. One measure of size is the element-element distance within the element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
